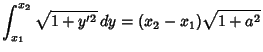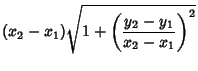Given two points in the Plane, find the curve which minimizes the distance between them. The Line Element
is given by
 |
(1) |
so the Arc Length between the points 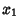 and
and 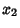 is
is
 |
(2) |
where
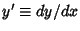 and the quantity we are minimizing is
and the quantity we are minimizing is
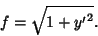 |
(3) |
Finding the derivatives gives
so the Euler-Lagrange Differential Equation becomes
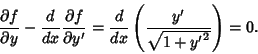 |
(6) |
Integrating and rearranging,
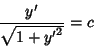 |
(7) |
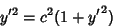 |
(8) |
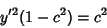 |
(9) |
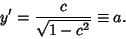 |
(10) |
The solution is therefore
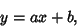 |
(11) |
which is a straight Line. Now verify that the Arc Length is indeed the straight-line distance between the points.
 and
and 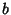 are determined from
are determined from
Writing (12) and (13) as a Matrix Equation gives
![\begin{displaymath}
\left[{\matrix{y_1\cr y_2\cr}}\right]=\left[{\matrix{x_1 & 1\cr x_2 & 1\cr}}\right]\left[{\matrix{a\cr b\cr}}\right]
\end{displaymath}](p2_889.gif) |
(14) |
so
as expected.
The shortest distance between two points on a Sphere is the so-called Great Circle distance.
See also Calculus of Variations, Great Circle, Point-Point Distance--1-D,
Point-Point Distance--3-D,
Point-Quadratic Distance, Tetrahedron Inscribing, Triangle Inscribing in a Circle
References
Arfken, G. Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 3rd ed. Orlando, FL: Academic Press, pp. 930-931, 1985.
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein
1999-05-25
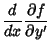
![$\displaystyle {d\over dx}[(1+{y'}^2)^{-1/2} y'],$](p2_879.gif)
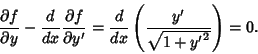
![$\displaystyle \left[\begin{array}{cc}x_1 & 1\\ x_2 & 1\end{array}\right]^{-1}\left[\begin{array}{c}y_1\\ y_2\end{array}\right]$](p2_891.gif)
![$\displaystyle {1\over{x_1-x_2}}\left[\begin{array}{cc}1 & -1\\ -x_2 & x_1\end{array}\right]^{-1}\left[\begin{array}{c}y_1\\ y_2\end{array}\right],$](p2_892.gif)