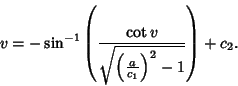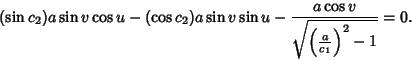The shortest path between two points on a Sphere, also known as an Orthodrome. To find the great
circle (Geodesic) distance between two points located at Latitude 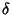 and Longitude
and Longitude 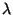 of
of
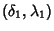 and
and
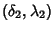 on a Sphere of Radius
on a Sphere of Radius 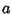 , convert Spherical
Coordinates to Cartesian Coordinates using
, convert Spherical
Coordinates to Cartesian Coordinates using
![\begin{displaymath}
{\bf r}_i=a\left[{\matrix{\cos\lambda_i\cos\delta_i\cr \sin\lambda_i\cos\delta_i\cr \sin\delta_i\cr}}\right].
\end{displaymath}](g_2008.gif) |
(1) |
(Note that the Latitude 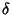 is related to the Colatitude
is related to the Colatitude 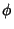 of Spherical Coordinates by
of Spherical Coordinates by
 , so the conversion to Cartesian Coordinates replaces
, so the conversion to Cartesian Coordinates replaces 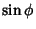 and
and 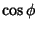 by
by
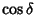 and
and 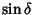 , respectively.) Now find the Angle
, respectively.) Now find the Angle 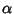 between
between 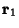 and
and 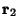 using
the Dot Product,
using
the Dot Product,
The great circle distance is then
![\begin{displaymath}
d=a\cos^{-1}[\cos\delta_1\cos\delta_2\cos(\lambda_1-\lambda_2)+\sin\delta_1\sin\delta_2].
\end{displaymath}](g_2020.gif) |
(3) |
For the Earth,  the equatorial Radius is
the equatorial Radius is 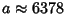 km, or 3963 (statute)
miles.
km, or 3963 (statute)
miles.  Unfortunately, the Flattening of the Earth cannot be taken into account in this simple
derivation, since the problem is considerably more complicated for a Spheroid or Ellipsoid (each of which has a
Radius which is a function of Latitude).
Unfortunately, the Flattening of the Earth cannot be taken into account in this simple
derivation, since the problem is considerably more complicated for a Spheroid or Ellipsoid (each of which has a
Radius which is a function of Latitude).
The equation of the great circle can be explicitly computed using the Geodesic formalism. Writing
gives the 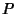 ,
, 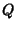 , and
, and 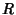 parameters of the Geodesic (which are just combinations of the Partial
Derivatives) as
parameters of the Geodesic (which are just combinations of the Partial
Derivatives) as
The Geodesic differential equation then becomes
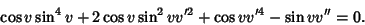 |
(9) |
However, because this is a special case of  with
with 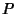 and
and 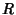 explicit functions of
explicit functions of  only, the
Geodesic solution takes on the special form
only, the
Geodesic solution takes on the special form
(Gradshteyn and Ryzhik 1979, p. 174, eqn. 2.599.6), which can be rewritten as
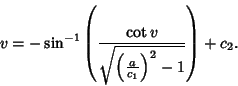 |
(11) |
It therefore follows that
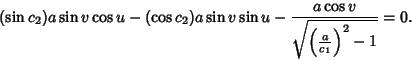 |
(12) |
This equation can be written in terms of the Cartesian Coordinates as
 |
(13) |
which is simply a Plane passing through the center of the Sphere and the two points on the surface of
the Sphere.
See also Geodesic, Great Sphere, Loxodrome, Mikusinski's Problem,
Orthodrome, Point-Point Distance--2-D, Sphere
References
Gradshteyn, I. S. and Ryzhik, I. M. Tables of Integrals, Series, and Products, 5th ed. San Diego, CA:
Academic Press, 1979.
Weinstock, R. Calculus of Variations, with Applications to Physics and Engineering. New York: Dover,
pp. 26-28 and 62-63, 1974.
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein
1999-05-25
![]() and Longitude
and Longitude ![]() of
of
![]() and
and
![]() on a Sphere of Radius
on a Sphere of Radius ![]() , convert Spherical
Coordinates to Cartesian Coordinates using
, convert Spherical
Coordinates to Cartesian Coordinates using
![\begin{displaymath}
{\bf r}_i=a\left[{\matrix{\cos\lambda_i\cos\delta_i\cr \sin\lambda_i\cos\delta_i\cr \sin\delta_i\cr}}\right].
\end{displaymath}](g_2008.gif)
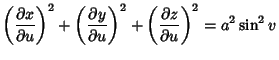
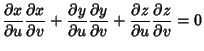
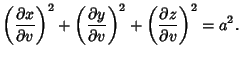
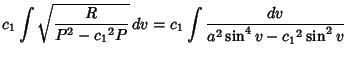
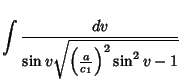
![$\displaystyle -\tan^{-1}\left[{\cos v\over\sqrt{\left({a\over c_1}\right)^2-1}}\right]+ c_2$](g_2029.gif)