|
|
|
The Wallis formula follows from the Infinite Product representation of the Sine
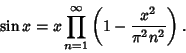 |
(1) |
![\begin{displaymath}
1 = {\pi\over 2} \prod_{n=1}^\infty \left[{1 - {1\over(2n)^2...
...over 2} \prod_{n=1}^\infty \left[{(2n)^2-1\over(2n)^2}\right],
\end{displaymath}](w_12.gif) |
(2) |
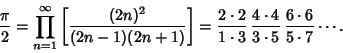 |
(3) |
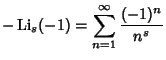 |
|||
| (4) | |||
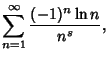 |
(5) |
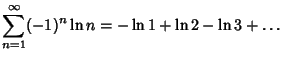 |
|||
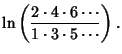 |
(6) |
| (7) |
|
|
|
|
|
(8) |
| (9) |
The q-Analog of the Wallis formula for ![]() is
is
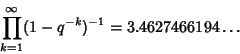 |
(10) |
See also Wallis Cosine Formula, Wallis Sine Formula
References
Abramowitz, M. and Stegun, C. A. (Eds.).
Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, 9th printing.
New York: Dover, p. 258, 1972.
Finch, S. ``Favorite Mathematical Constants.'' http://www.mathsoft.com/asolve/constant/dig/dig.html
Kenney, J. F. and Keeping, E. S. Mathematics of Statistics, Pt. 2, 2nd ed. Princeton, NJ: Van Nostrand, pp. 63-64, 1951.
|
|
|
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein