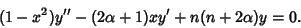 |
(1) |
Alternate forms are
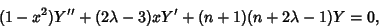 |
(2) |
where
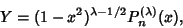 |
(3) |
![\begin{displaymath}
{d^2u\over dx^2}+\left[{{(n+\lambda)^2\over 1-x^2}+{{\textst...
...lambda^2+{\textstyle{1\over 4}}x^2\over (1-x^2)^2}}\right]u=0,
\end{displaymath}](u_48.gif) |
(4) |
where
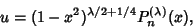 |
(5) |
and
![\begin{displaymath}
{d^2u\over d\theta^2}+\left[{(n+\lambda)^2+{\lambda(1-\lambda)\over\sin^2\theta}}\right]u=0,
\end{displaymath}](u_50.gif) |
(6) |
where
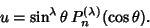 |
(7) |
The solutions are the Ultraspherical Functions
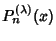 . For integral
. For integral  with
with 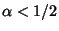 , the
function converges to the Ultraspherical Polynomials
, the
function converges to the Ultraspherical Polynomials
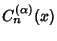 .
.
References
Morse, P. M. and Feshbach, H. Methods of Theoretical Physics, Part I. New York:
McGraw-Hill, pp. 547-549, 1953.
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein
1999-05-26