|
|
|
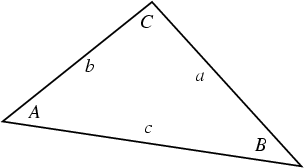
Let ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() be the lengths of the legs of a Triangle opposite Angles
be the lengths of the legs of a Triangle opposite Angles ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() .
Then the law of cosines states
.
Then the law of cosines states
| (1) |
| (2) | |||
| (3) | |||
| (4) |
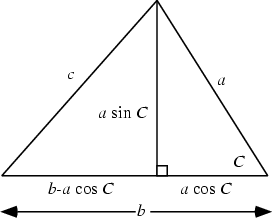
The formula can also be derived using a little geometry and simple algebra. From the above diagram,
| (5) |
The law of cosines for the sides of a Spherical Triangle states that
| (6) | |||
| (7) | |||
| (8) |
| (9) | |||
| (10) | |||
| (11) |
See also Law of Sines, Law of Tangents
References
Abramowitz, M. and Stegun, C. A. (Eds.).
Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, 9th printing.
New York: Dover, p. 79, 1972.
Beyer, W. H. CRC Standard Mathematical Tables, 28th ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp. 148-149, 1987.
|
|
|
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein