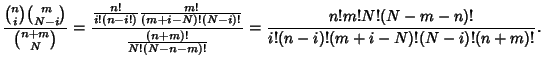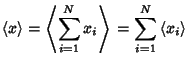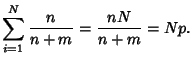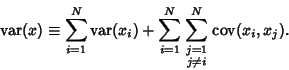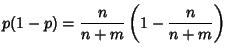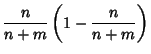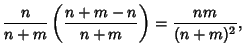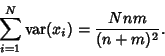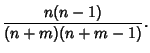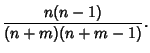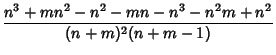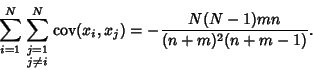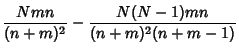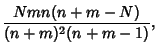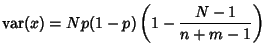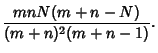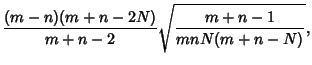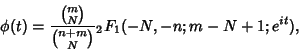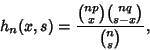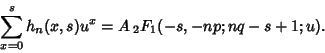Let there be 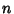 ways for a successful and
ways for a successful and  ways for an unsuccessful trial out of a total of
ways for an unsuccessful trial out of a total of  possibilities.
Take
possibilities.
Take 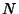 samples and let
samples and let 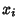 equal 1 if selection
equal 1 if selection  is successful and 0 if it is not. Let
is successful and 0 if it is not. Let  be the total number of
successful selections,
be the total number of
successful selections,
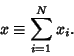 |
(1) |
The probability of  successful selections is then
successful selections is then
The  th selection has an equal likelihood of being in any trial, so the fraction of acceptable selections
th selection has an equal likelihood of being in any trial, so the fraction of acceptable selections 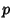 is
is
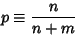 |
(3) |
 |
(4) |
The expectation value of  is
is
The Variance is
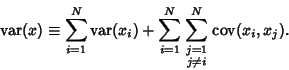 |
(6) |
Since 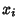 is a Bernoulli variable,
is a Bernoulli variable,
so
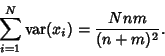 |
(8) |
For 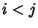 , the Covariance is
, the Covariance is
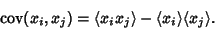 |
(9) |
The probability that both  and
and 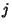 are successful for
are successful for 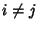 is
is
But since 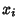 and
and 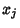 are random Bernoulli variables (each 0 or 1), their product is
also a Bernoulli variable. In order for
are random Bernoulli variables (each 0 or 1), their product is
also a Bernoulli variable. In order for 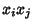 to be 1, both
to be 1, both 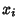 and
and 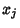 must be
1,
must be
1,
Combining (11) with
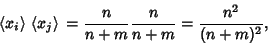 |
(12) |
gives
There are a total of  terms in a double summation over
terms in a double summation over 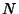 . However,
. However, 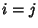 for
for 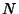 of these, so there are a total
of
of these, so there are a total
of
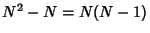 terms in the Covariance summation
terms in the Covariance summation
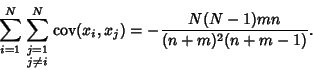 |
(14) |
Combining equations (6), (8), (11), and (14) gives the Variance
so the final result is
 |
(16) |
and, since
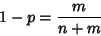 |
(17) |
and
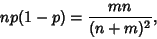 |
(18) |
we have
The Skewness is
and the Kurtosis
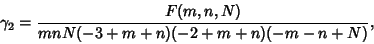 |
(21) |
where
The Generating Function is
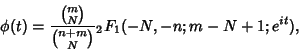 |
(23) |
where
 is the Hypergeometric Function.
is the Hypergeometric Function.
If the hypergeometric distribution is written
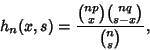 |
(24) |
then
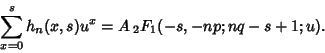 |
(25) |
References
Beyer, W. H. CRC Standard Mathematical Tables, 28th ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp. 532-533, 1987.
Spiegel, M. R. Theory and Problems of Probability and Statistics.
New York: McGraw-Hill, pp. 113-114, 1992.
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein
1999-05-25
![]() ways for a successful and
ways for a successful and ![]() ways for an unsuccessful trial out of a total of
ways for an unsuccessful trial out of a total of ![]() possibilities.
Take
possibilities.
Take ![]() samples and let
samples and let ![]() equal 1 if selection
equal 1 if selection ![]() is successful and 0 if it is not. Let
is successful and 0 if it is not. Let ![]() be the total number of
successful selections,
be the total number of
successful selections,
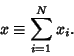
![$\displaystyle {\hbox{[\char93 ways for $i$\ successes][\char93 ways for $N-i$\ unsuccesses]}\over\hbox{[total number of ways to select]}}$](h_2229.gif)