|
|
|
An intrinsic property of a space independent of the coordinate system used to describe it. The Gaussian curvature of a
Regular Surface in ![]() at a point p is formally defined as
at a point p is formally defined as
| (1) |
If
![]() is a Regular Patch, then the Gaussian curvature is given by
is a Regular Patch, then the Gaussian curvature is given by
| (2) |
| (3) |
| (4) |
| (5) |
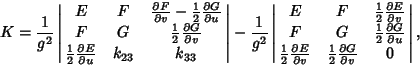 |
(6) |
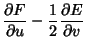 |
(7) | ||
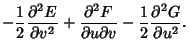 |
(8) |
![$\displaystyle {1\over 2g}\left[{2{\partial^2F\over\partial u\partial v}-{\parti...
...al G\over\partial u}}\right)-\left({\partial E\over\partial v}\right)^2}\right]$](g_664.gif) |
|||
![$\displaystyle + {F\over 4g_2}\left[{{\partial E\over\partial u}{\partial G\over...
...\left({2{\partial F\over\partial v}-{\partial G\over\partial u}}\right)}\right]$](g_666.gif) |
|||
![$\displaystyle -{E\over 4g^2}\left[{{\partial G\over\partial v}\left({2{\partial...
...l E\over\partial v}}\right)-\left({\partial G\over\partial u}\right)^2}\right].$](g_667.gif) |
(9) |
The Gaussian curvature is also given by
| (10) |
![$\displaystyle {[\hat{\bf N}\,\hat{\bf N}_1\,\hat{\bf N}_2]\over\sqrt{g}} = {\epsilon^{ij} [\hat{\bf N}\,\hat{\bf T}\,\hat{\bf T}_i]_j\over \sqrt{g}},$](g_669.gif) |
(11) |
| (12) |
| (13) |
The Gaussian curvature ![]() and Mean Curvature
and Mean Curvature ![]() satisfy
satisfy
| (14) |
| (15) |
If p is a point on a Regular Surface
![]() and
and
![]() and
and
![]() are tangent
vectors to
are tangent
vectors to ![]() at p, then the Gaussian curvature of
at p, then the Gaussian curvature of ![]() at p is related to the Shape Operator
at p is related to the Shape Operator ![]() by
by
| (16) |
| (17) |
For a Sphere, the Gaussian curvature is ![]() . For Euclidean Space, the Gaussian curvature is
. For Euclidean Space, the Gaussian curvature is ![]() . For
Gauss-Bolyai-Lobachevsky Space, the Gaussian curvature is
. For
Gauss-Bolyai-Lobachevsky Space, the Gaussian curvature is ![]() . A Flat Surface is a Regular Surface
and special class of Minimal Surface on which Gaussian curvature vanishes everywhere.
. A Flat Surface is a Regular Surface
and special class of Minimal Surface on which Gaussian curvature vanishes everywhere.
A point p on a Regular Surface ![]() is classified based on the sign of
is classified based on the sign of ![]() as given in the
following table (Gray 1993, p. 280), where
as given in the
following table (Gray 1993, p. 280), where ![]() is the Shape Operator.
is the Shape Operator.
| Sign | Point |
| Elliptic Point | |
| Hyperbolic Point | |
| Parabolic Point | |
| Planar Point |
A surface on which the Gaussian curvature ![]() is everywhere Positive is called Synclastic, while a
surface on which
is everywhere Positive is called Synclastic, while a
surface on which ![]() is everywhere Negative is called Anticlastic. Surfaces with constant Gaussian
curvature include the Cone, Cylinder, Kuen Surface,
Plane, Pseudosphere, and Sphere. Of these, the Cone
and Cylinder
are the only Flat Surfaces of Revolution.
is everywhere Negative is called Anticlastic. Surfaces with constant Gaussian
curvature include the Cone, Cylinder, Kuen Surface,
Plane, Pseudosphere, and Sphere. Of these, the Cone
and Cylinder
are the only Flat Surfaces of Revolution.
See also Anticlastic, Brioschi Formula, Developable Surface, Elliptic Point, Flat Surface, Hyperbolic Point, Integral Curvature, Mean Curvature, Metric Tensor, Minimal Surface, Parabolic Point, Planar Point, Synclastic, Umbilic Point
References
Geometry Center. ``Gaussian Curvature.''
http://www.geom.umn.edu/zoo/diffgeom/surfspace/concepts/curvatures/gauss-curv.html.
Gray, A. ``The Gaussian and Mean Curvatures'' and ``Surfaces of Constant Gaussian Curvature.'' §14.5 and Ch. 19 in
Modern Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces.
Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp. 279-285 and 375-387, 1993.
|
|
|
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein