If 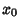 is an ordinary point of the Ordinary Differential Equation, expand
is an ordinary point of the Ordinary Differential Equation, expand 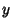 in
a Taylor Series about
in
a Taylor Series about 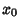 , letting
, letting
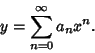 |
(1) |
Plug 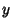 back into the ODE and group the Coefficients by
Power. Now, obtain a Recurrence Relation for the
back into the ODE and group the Coefficients by
Power. Now, obtain a Recurrence Relation for the 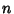 th
term, and write the Taylor Series in terms of the
th
term, and write the Taylor Series in terms of the 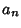 s. Expansions for the first few derivatives are
s. Expansions for the first few derivatives are
If 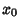 is a regular singular point of the Ordinary Differential Equation,
is a regular singular point of the Ordinary Differential Equation,
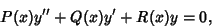 |
(5) |
solutions may be found by the Frobenius method or by expansion in a Laurent Series. In the Frobenius method, assume
a solution of the form
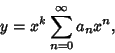 |
(6) |
so that
Now, plug 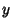 back into the ODE and group the Coefficients by Power to obtain a recursion
Formula for the
back into the ODE and group the Coefficients by Power to obtain a recursion
Formula for the 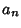 th term, and then write the Taylor Series in terms of the
th term, and then write the Taylor Series in terms of the 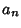 s. Equating the
s. Equating the 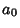 term to
0 will produce the so-called Indicial Equation, which will give the allowed values of
term to
0 will produce the so-called Indicial Equation, which will give the allowed values of  in the Taylor Series.
in the Taylor Series.
Fuchs's Theorem guarantees that at least one Power series solution will be obtained when applying the Frobenius
method if the expansion point is an ordinary, or regular, Singular Point. For a regular
Singular Point, a Laurent Series expansion can also be used. Expand 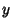 in a
Laurent Series, letting
in a
Laurent Series, letting
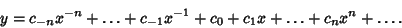 |
(10) |
Plug 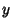 back into the ODE and group the Coefficients by Power. Now, obtain a recurrence
Formula for the
back into the ODE and group the Coefficients by Power. Now, obtain a recurrence
Formula for the  th term, and write the Taylor Expansion in terms of the
th term, and write the Taylor Expansion in terms of the  s.
s.
See also Fuchs's Theorem, Ordinary Differential Equation
References
Arfken, G. ``Series Solutions--Frobenius' Method.'' §8.5 in Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 3rd ed.
Orlando, FL: Academic Press, pp. 454-467, 1985.
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein
1999-05-26
![]() is an ordinary point of the Ordinary Differential Equation, expand
is an ordinary point of the Ordinary Differential Equation, expand ![]() in
a Taylor Series about
in
a Taylor Series about ![]() , letting
, letting
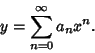
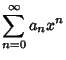
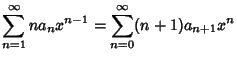

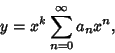
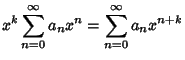

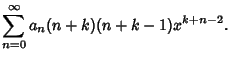
![]() in a
Laurent Series, letting
in a
Laurent Series, letting