A divisor of a number 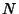 is a number
is a number 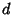 which Divides
which Divides 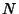 , also called a Factor. The total number of
divisors for a given number
, also called a Factor. The total number of
divisors for a given number 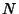 can be found as follows. Write a number in terms of its Prime Factorization
can be found as follows. Write a number in terms of its Prime Factorization
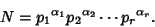 |
(1) |
For any divisor 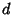 of
of 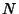 ,
, 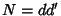 where
where
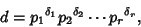 |
(2) |
so
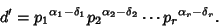 |
(3) |
Now,
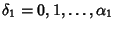 , so there are
, so there are 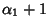 possible values. Similarly, for
possible values. Similarly, for 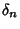 , there are
, there are
 possible values, so the total number of divisors
possible values, so the total number of divisors 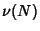 of
of 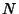 is given by
is given by
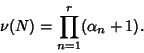 |
(4) |
The function 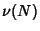 is also sometimes denoted
is also sometimes denoted 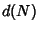 or
or 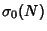 .
The product of divisors can be found by writing
the number
.
The product of divisors can be found by writing
the number 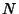 in terms of all possible products
in terms of all possible products
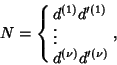 |
(5) |
so
and
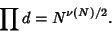 |
(7) |
The Geometric Mean of divisors is
![\begin{displaymath}
G\equiv \left({\prod d}\right)^{1/\nu(N)} = [N^{\nu(n)/2}]^{1/\nu(N)} = \sqrt{N}.
\end{displaymath}](d2_1231.gif) |
(8) |
The sum of the divisors can be found as follows. Let 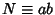 with
with 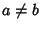 and
and 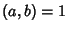 . For any divisor
. For any divisor 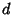 of
of
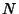 ,
, 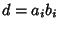 , where
, where 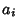 is a divisor of
is a divisor of  and
and 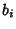 is a divisor of
is a divisor of 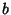 . The divisors of
. The divisors of  are 1,
are 1, 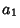 ,
, 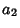 ,
..., and
,
..., and  . The divisors of
. The divisors of 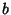 are 1,
are 1, 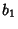 ,
, 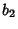 , ...,
, ..., 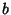 . The sums of the divisors are then
. The sums of the divisors are then
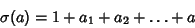 |
(9) |
 |
(10) |
For a given 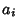 ,
,
 |
(11) |
Summing over all 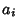 ,
,
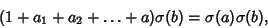 |
(12) |
so
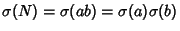 . Splitting
. Splitting  and
and 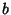 into prime factors,
into prime factors,
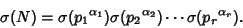 |
(13) |
For a prime Power
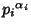 , the divisors are 1,
, the divisors are 1, 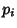 ,
, 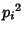 , ...,
, ...,
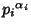 , so
, so
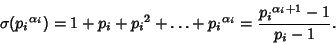 |
(14) |
For 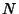 , therefore,
, therefore,
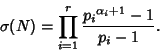 |
(15) |
For the special case of 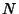 a Prime, (15) simplifies to
a Prime, (15) simplifies to
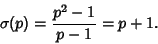 |
(16) |
For 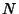 a Power of two, (15) simplifies to
a Power of two, (15) simplifies to
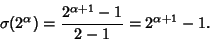 |
(17) |
The Arithmetic Mean is
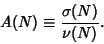 |
(18) |
The Harmonic Mean is
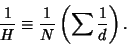 |
(19) |
But 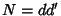 , so
, so  and
and
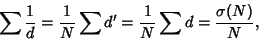 |
(20) |
and we have
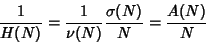 |
(21) |
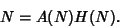 |
(22) |
Given three Integers chosen at random, the probability that no common factor will divide them all is
![\begin{displaymath}[\zeta(3)]^{-1}\approx 1.20206^{-1} \approx 0.831907,
\end{displaymath}](d2_1258.gif) |
(23) |
where 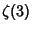 is Apéry's Constant.
is Apéry's Constant.
Let 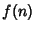 be the number of elements in the greatest subset of
be the number of elements in the greatest subset of ![$[1,n]$](d2_1261.gif) such that none of its elements are divisible by
two others. For
such that none of its elements are divisible by
two others. For 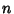 sufficiently large,
sufficiently large,
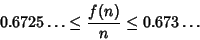 |
(24) |
(Le Lionnais 1983, Lebensold 1976/1977).
See also Aliquant Divisor, Aliquot Divisor, Aliquot Sequence, Dirichlet Divisor Problem,
Divisor Function, e-Divisor, Exponential Divisor, Greatest Common Divisor, Infinary
Divisor, k-ary Divisor, Perfect Number, Proper Divisor, Unitary Divisor
References
Guy, R. K. ``Solutions of 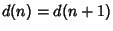 .'' §B18 in
Unsolved Problems in Number Theory, 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag, pp. 73-75, 1994.
.'' §B18 in
Unsolved Problems in Number Theory, 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag, pp. 73-75, 1994.
Le Lionnais, F. Les nombres remarquables. Paris: Hermann, p. 43, 1983.
Lebensold, K. ``A Divisibility Problem.'' Studies Appl. Math. 56, 291-294, 1976/1977.
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein
1999-05-24
![]() is a number
is a number ![]() which Divides
which Divides ![]() , also called a Factor. The total number of
divisors for a given number
, also called a Factor. The total number of
divisors for a given number ![]() can be found as follows. Write a number in terms of its Prime Factorization
can be found as follows. Write a number in terms of its Prime Factorization
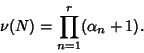
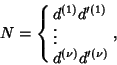
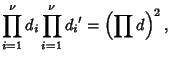
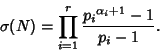
![]() be the number of elements in the greatest subset of
be the number of elements in the greatest subset of ![]() such that none of its elements are divisible by
two others. For
such that none of its elements are divisible by
two others. For ![]() sufficiently large,
sufficiently large,
![]() .'' §B18 in
Unsolved Problems in Number Theory, 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag, pp. 73-75, 1994.
.'' §B18 in
Unsolved Problems in Number Theory, 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag, pp. 73-75, 1994.