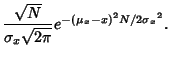Let
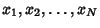 be a set of
be a set of 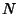 Independent random variates and each
Independent random variates and each 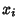 have an arbitrary probability distribution
have an arbitrary probability distribution
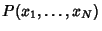 with Mean
with Mean 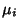 and a finite Variance
and a finite Variance
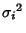 . Then the normal form variate
. Then the normal form variate
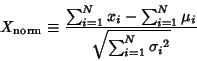 |
(1) |
has a limiting distribution which is Normal (Gaussian)
with Mean 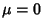 and Variance
and Variance 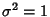 . If conversion to normal form is not performed, then the
variate
. If conversion to normal form is not performed, then the
variate
 |
(2) |
is Normally Distributed with 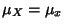 and
and
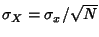 . To prove
this, consider the Inverse Fourier Transform of
. To prove
this, consider the Inverse Fourier Transform of 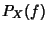 .
.
Now write
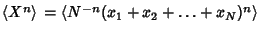
|
|
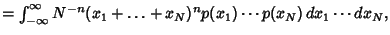
|
|
|
|
(4) |
so we have
Now expand
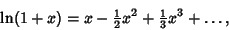 |
(6) |
so
since
Taking the Fourier Transform,
This is of the form
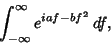 |
(11) |
where
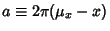 and
and
 . But, from
Abramowitz and Stegun (1972, p. 302, equation 7.4.6),
. But, from
Abramowitz and Stegun (1972, p. 302, equation 7.4.6),
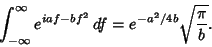 |
(12) |
Therefore,
But
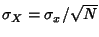 and
and 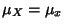 , so
, so
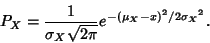 |
(14) |
The ``fuzzy'' central limit theorem says that data which are influenced by many small and unrelated random effects are
approximately Normally Distributed.
See also Lindeberg Condition, Lindeberg-Feller Central Limit Theorem, Lyapunov Condition
References
Abramowitz, M. and Stegun, C. A. (Eds.).
Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, 9th printing.
New York: Dover, 1972.
Spiegel, M. R. Theory and Problems of Probability and Statistics.
New York: McGraw-Hill, pp. 112-113, 1992.
Zabell, S. L. ``Alan Turing and the Central Limit Theorem.'' Amer. Math. Monthly 102, 483-494, 1995.
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein
1999-05-26
![]() be a set of
be a set of ![]() Independent random variates and each
Independent random variates and each ![]() have an arbitrary probability distribution
have an arbitrary probability distribution
![]() with Mean
with Mean ![]() and a finite Variance
and a finite Variance
![]() . Then the normal form variate
. Then the normal form variate
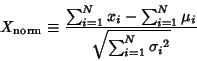

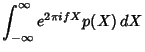
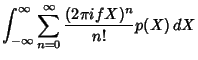
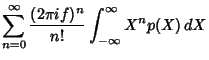
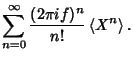
![$= \left[{\int_{-\infty}^\infty e^{2\pi i f x/N}p(x)\,dx}\right]^N$](c1_929.gif)
![$= \left\{{\int_{-\infty}^\infty \left[{1+\left({2\pi i f \over N}\right)x +{1\over 2}\left({2\pi i f \over N}\right)^2 x^2 +\ldots}\right]p(x)\,dx}\right\}^N$](c1_930.gif)
![$= \left[{\int_{-\infty}^\infty p(x)\,dx+{2\pi i f\over N}\int_{-\infty}^\infty ...
...)^2\over 2N^2} \int_{-\infty}^\infty x^2p(x)\,dx+{\mathcal O}(N^{-3})}\right]^N$](c1_931.gif)
![$= \left[{1+{2\pi i f\over N}\left\langle{x}\right\rangle{}-{(2\pi f)^2\over 2N^2}\left\langle{x^2}\right\rangle{}+{\mathcal O}(N^{-3})}\right]^N$](c1_932.gif)
![$\displaystyle \mathop{\rm exp}\nolimits \left\{{N\left[{{2\pi if\over N}\left\l...
...ver N^2}\left\langle{x}\right\rangle{}^2 +{\mathcal O}(N^{-3})}\right]}\right\}$](c1_936.gif)
![$\displaystyle \mathop{\rm exp}\nolimits \left[{2\pi if\left\langle{x}\right\ran...
...angle{}-\left\langle{x}\right\rangle{}^2)\over 2N}+{\mathcal O}(N^{-2})}\right]$](c1_937.gif)
![$\displaystyle \mathop{\rm exp}\nolimits \left[{2\pi if\mu_x-{(2\pi f)^2{\sigma_x}^2\over 2N}}\right],$](c1_938.gif)
![$\displaystyle \int_{-\infty}^\infty e^{-2\pi ifx}{\mathcal F}^{-1}[P_X(f)]\,df$](c1_944.gif)

![$\displaystyle \sqrt{\pi\over{(2\pi\sigma_x)^2\over 2N}} \mathop{\rm exp}\nolimits \left\{{-[{2\pi(\mu_x-x)]^2}\over {4{(2\pi\sigma_x)^2\over 2N}}}\right\}$](c1_950.gif)
![$\displaystyle \sqrt{2\pi N\over 4\pi^2{\sigma_x}^2} \mathop{\rm exp}\nolimits \left[{-{4\pi^2(\mu_x-x)^2 2N\over 4\cdot 4\pi^2{\sigma_x}^2}}\right]$](c1_951.gif)